Managing Your Blood Sugar
Know How to Manage Your Blood Sugar
When you have diabetes your body can no longer control the amount of sugar in your blood. Your body either no longer produces insulin (type 1 diabetes) or no longer reacts to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Without insulin, your body can no longer lower your blood sugar when it gets too high.
Manage Diabetes
3 things you should know to manage your blood sugar:
- How to use a glucometer to measure your blood sugar
- When to check your blood sugar at home
- What an A1c blood test is and what the results mean
When your blood sugar levels get too high, it can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, or amputation.
Learn more about the health problems that diabetes can lead to »
Knowing what your blood sugar is in response to taking your medicine, eating, or exercising helps you understand how your medicine and healthy habits are helping you manage your diabetes. A glucometer is one tool to help you manage your blood sugar.
Find out how a glucometer helps you manage your blood sugar »
What is Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)?
Low blood sugar (also known as hypoglycemia) means there is not enough sugar in your blood. Low blood sugar happens when your blood sugar drops below 4 mmol/L, but you may have signs of low blood sugar at different levels. This is a dangerous condition because your body needs sugar to function.
If your blood sugar gets too low you can become disoriented or confused, and you may even lose consciousness (go into a coma) or die. This is called severe hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia happens when your blood sugar is so low you cannot treat it yourself with fast acting carbohydrates or glucagon (a medicine sometimes prescribed by doctors for people who are prone to very low blood sugar).
Safety Alert
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) is a medical emergency.
- Always carry a fast-acting carbohydrate with you. Fast-acting carbohydrates (such as gummies, over-the-counter sugar pills, and fruit in juice) raise your blood sugar quickly.
- Wear jewelry that lets people know you have diabetes. A medical alert bracelet is one type of this jewelry.
Teach your family members and friends how to help you when you can no longer treat your low blood sugar by yourself. They need to know this is a medical emergency and you need help right away.
You are at high risk for low blood sugar if you:
- are taking insulin
- are taking a medicine from the Secretagogue class of medications like:
- Diamicron (Gliclazide)
- Amaryl (Glimepiride)
- Glyburide (Diabeta)
- Repaglinide (Gluconorm)
- start a new exercise program and are prescribed insulin or a medicine from the Secretagogue class of medicines
- have had episodes of low blood sugar in the past
- have an A1c of less than 6 percent (%)
- do not get any of the signs of low blood sugar when your blood sugar is low
People have different signs of low blood sugar and the signs can happen at different levels. For example, some people may have signs at 6mmol/L while others have signs at 4mmol/L. Be aware of the signs of low blood sugar below:
- trembling or shaking
- dizzy
- anxiety (nervous and fearful)
- sweating
- nausea
- hard time thinking
- feeling tired (drowsy)
- tingling in your face or hands
- hunger
- disoriented (confused)
- headache
- difficulty speaking
- changes to your vision
- faster heart beat than usual (palpitations)
- seizures or loss of consciousness (with severe hypoglycemia)
Some people have low blood sugar levels and do not have any of the signs listed. In this case, it is important to check your blood sugar often, especially before driving a car or other motorized vehicle.
Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or diabetes educator the questions below to learn what you can do to prevent low blood sugar:
- What is the right amount of diabetes medicine for me?
- How do I time my diabetes medicine with my food?
- When is my diabetes medicine working the hardest?
- How often do I check my blood sugar?
- How much exercise lowers my blood sugar?
- How will I know if I have low blood sugar?
The tips below can also help prevent low blood sugar:
- Know the signs of low blood sugar.
- Check your blood sugar often. You may not have any signs of low blood sugar.
- If you take insulin or a medicine from the Secretagogue class of medicines, check your blood sugar before you exercise.
- If your blood sugar is less than 5.5 mmol/L, have a snack that contains protein and a slow acting carbohydrate (such as a slice of whole grain bread with peanut butter). Slow acting carbohydrate slowly raises your blood sugar to prevent an episode of low blood sugar.
- Carry a fast acting carbohydrate with you at all times just in case you need it. Fast acting carbohydrate raises your blood sugar quickly.
Teach your family members and friends how to help you when you can no longer treat your blood sugar by yourself.
There are two ways to know you have low blood sugar:
- you have any signs of low blood sugar, or
- your glucometer reading is less than 4.0 mmol/L
If you have low blood sugar:
- Act quickly. Do not wait.
- Stop what you are doing and sit down. Test your blood sugar with your glucometer if you have not already done so.
- Eat or drink 15 grams of fast acting carbohydrate. Fast acting carbohydrates raise your blood sugar quickly.
Examples of fast acting carbohydrates are- 15 grams of sugar tablets
- ¾ cup (175 ml) of juice
- ¾ cup (175 ml) regular pop (soft drink)
- 3 teaspoons or 3 packets of sugar dissolved in water
- 6 LifeSavers
- 1 tablespoon (15 ml) of honey
- Wait 15 minutes.
- Test your blood sugar again.
- If your blood sugar is still below 4 mmol/L take another 15 grams of fast acting carbohydrate.
- Wait another 15 minutes and check your blood sugar again.
- Repeat this step until your blood sugar is higher than 4 mmol/L.
- When your blood sugar is above 4 mmol/L, eat your usual meal.
- Follow your regular meal schedule. Have a snack if your meal is more than 1 hour away. This snack should have a slower acting carbohydrate and protein like a slice of wholegrain bread with reduced fat cheese. Slower acting carbohydrates raise your blood sugar slowly over a period of time. This will prevent another episode of low blood sugar.
If you had a severe episode of hypoglycemia in the past, your doctor may tell you to treat any future episodes with greater amounts of fast acting carbohydrate or glucagon (a medicine prescribed by your doctor).
If your blood sugar goes too low you will likely need help. It is important that you let your family and friends know how to help you when you can no longer help yourself (for example, you become disoriented, have a seizure or lose consciousness). This is a medical emergency.
Wear jewelry that lets people know you have diabetes. A medical alert bracelet is one type of this jewelry.
Having low blood sugar is a risk to your safety and health:
- You are at a greater risk of a vehicle accident if your blood sugar is low. Do not use machinery or drive a vehicle if your blood sugar is low.
- Having an episode of low blood sugar puts you at risk of not being able to notice the next time your blood sugar goes low.
- You may have a higher risk of dementia (loss of memory or thinking skills) if you have type 2 diabetes and have many severe episodes of low blood sugar.
Reflect on your low blood sugar episode to help prevent another episode. Use the reflection chart below to answer questions about your low blood sugar episode.
| Reflection Questions | Morning | Afternoon | Evening |
|---|---|---|---|
| When did I take my diabetes medicine today? | |||
| Did I take a different amount of my medicine today? | |||
| Am I taking a new medicine? | |||
| How long did I exercise for today? | |||
| What time did I exercise today? | |||
| What did I eat and drink today? | |||
| What time did I eat? |
Once you complete the chart, take it to your doctor, pharmacist, or diabetes educator. They can help you make changes to prevent low blood sugar. This can include changes to your medicines, food, or exercise.
Safety Alert
Check your blood sugar before driving. Your blood sugar should be higher than 5 mmol/L. This will prevent you from having low blood sugar while driving.
This check is especially important if you are taking insulin or a medicine from the Secretagogue class of medicines (like Glyburide).
Follow the tips below to stay safe while you drive:
- Check your blood sugar every 4 hours on long drives.
- Carry a fast acting carbohydrate (such as sugar tablets, juice or pop) with you at all times so that you can treat low blood sugar quickly.
- Your blood sugar must stay above 5 mmol/L for 45 minutes or longer before you drive if you just treated a low blood sugar episode.
What is High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)?
High blood sugar (also called hyperglycemia) means your blood sugar level is higher than normal. Over time, too much sugar in your blood leads to serious health problems.
Safety Alert
Get medical help right away if you get very high blood sugar. Very high blood sugar can be a sign of a serious and deadly health problem called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
If you take insulin, are ill, and have high blood sugar, get medical help right away.
You are at high risk for high blood sugar if you:
- did not take enough diabetes medicine
- are ill (with a cold, infection, or having surgery)
- have stress
- have too much sugary food or drinks
- take medicines that make your sugar high (such as steroids and some psychiatric medicines)
Everyone has different signs of high blood sugar. You may have any number of the signs listed below.
High blood sugar signs may include:
- being thirsty
- feeling tired
- needing to pee more
- having an upset stomach, or stomach pain
- vomiting
- having blurry vision
- you smell like apple cider
Many people do not have the signs of high blood sugar. It is important to check your blood sugar regularly so that you know how well you are managing your diabetes between A1c tests. Talk to your doctor about how often you should check your blood sugar.
You can prevent high blood sugar by:
- taking your diabetes medicines as prescribed.
Find out more about diabetes medicines » - avoiding sugary foods and drinks.
Find out how to avoid sugary foods and drinks » - managing your stress and depression.
Find out what you can do to manage your stress » - doing exercise.
Find out what you can do to be more active » - following the guidelines your doctor gave you for when you are ill.
- talking to your pharmacist about how you can remember to take your medicines.
Treat high blood sugar by taking your diabetes medicines as prescribed. Talk to your doctor if you cannot get your blood sugar into a normal range for you. You may need to:
- have your diabetes medicines changed
- change something in your diet
- exercise more regularly
- manage your stress, depression better
- avoid smoking or breathing second-hand smoke
- check your blood sugar more often
Safety Alert
If you have high blood sugar and you are ill (cold, infection or surgery) do not stop taking your diabetes medicines. It is important that you keep taking your insulin if it is prescribed to you. If you do not take your insulin you are at risk for a serious and deadly health problem called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
Get medical help if you are ill, take insulin and have high blood sugar.
Continue to take your diabetes medicines (especially if you are prescribed insulin) if you are ill. When you are ill, your blood sugar will likely be high even if you are eating less than normal or vomiting (throwing up). Check your blood sugar more often if you are ill, have an infection, or are undergoing surgery.
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or diabetes educator about how to manage your diabetes when you are ill. They may adjust the amount of diabetes medicine you take. They will provide you with specific guidelines to follow when you are ill.
Talk to your doctor so you know:
- how to adjust the amount of diabetes medicine you take
- what medicines you should stop if you are dehydrated (your body does not have enough water)
- how often to check your blood sugar
- when to get medical help
Follow these general tips when you are ill:
- Take time to rest.
- Check your blood sugar more often and before meals.
- Do not exercise until you feel better.
- Drink lots of water. Drink about ½ to 1 cup of fluids each hour.
- Other medical conditions may tell you to limit your fluids. Do not drink more fluids if this is true. Talk to your doctor for more information.
- Take your diabetes medicine when you are sick. This will help control your blood sugar and prevent health problems.
- Get medical help right away if your blood sugar remains high.
Check Your Blood Sugar
Ask your doctor how often you need to check your blood sugar at home with your glucometer. Your doctor can order an A1c blood test to understand your blood sugar control over the last 3 months.
Talk to your doctor to learn how often to check your blood sugar. You will have to check your blood sugar more often if:
- you take insulin
- you take a Secretagogue medicine
- you have changes to your diabetes medicines
- you have episodes of very low blood sugar, called hypoglycemia
- you have the signs of low blood sugar
- you have the signs of high blood sugar
- you are ill (with a cold, infection or having surgery)
- you started a new exercise program or progressed your program
- your A1c is not within the normal range
Learn when to check your blood sugar when you exercise »
Learn about insulin and Secretatgogue medicines »
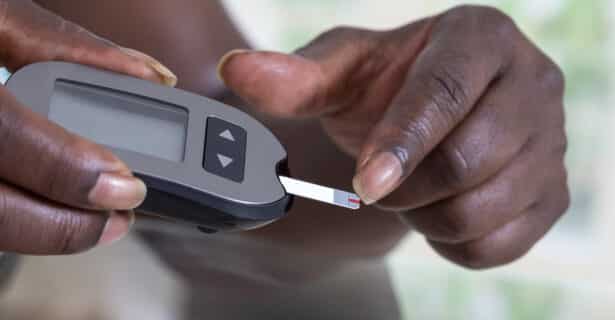
What is a glucometer and how does it work?
A glucometer is a tool that measures your blood sugar. It measures how much sugar is in a small drop of blood from your finger.
At any time, each blood cell has the same amount of sugar as the other blood cells. Because of this, measuring the sugar in one drop of blood is the same as measuring the level in many drops.
Once the sample of blood is taken, a reading appears on the glucometer screen. The reading will be in mmol/L, such as 5.2 mmol/L. This reading tells your blood sugar level at that exact moment.
How do I use the information from the glucometer?
Ask your doctor how often you need to check your blood sugar. Be sure to record your blood sugar numbers so you can see how your body responds to:
- what you eat and drink
- your diabetes medicine(s)
- your exercise and activity levels
- your stress level
- illness (a cold, infection, or surgery)
Where can I buy a glucometer?
You can buy a glucometer and testing strips at most pharmacies. There are many different models of glucometers so talk to your pharmacist about which model is best for you.
A1c and Blood Sugar
An A1c test uses a sample of your blood to measure your blood sugar control over the last 3 months. The test counts the number of blood cells with sugar attached to them.
Red blood cells use sugar (glucose) as their only source of fuel. These cells live up to 120 days (about 4 months). In a blood lab test, the cells can show the average amount of sugar they were exposed to during their lifetime to give your A1c level.
You and your doctor can use your A1c to guide how you manage your diabetes.
Learn how to use the results of your A1C test to know your blood sugar control »
Medical Identification Jewelry
Medical identification jewelry is jewelry (such as a bracelet or necklace) with a small medical emblem. On the back, it tells people you have diabetes. This jewelry can save your life.
In an emergency, such as if you go unconscious, the bracelet will tell others you have diabetes. This will allow people to know how to help you quickly. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist for more information.